How the right high-temperature insulation ensures better exhaust gas emissions
With proper exhaust tract insulation, all emission targets can be met and the efficiency of the exhaust gas aftertreatment system can be increased.

Exhaust gas aftertreatment
Exhaust gas aftertreatment is a central component in the modern development of internal combustion engines. This includes all processes in which the combustion gases are cleaned by mechanical, catalytic or chemical means after leaving the combustion chamber. The aim of exhaust gas cleaning is to turn the pollutants produced during combustion into harmless exhaust gases.
There are various technologies and methods that can be used in exhaust gas aftertreatment to reduce pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOX), hydrocarbons (HC) or particulate matter. Most notably, these include exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) and exhaust gas aftertreatment with selective catalytic reduction (SCR) with the addition of AdBlue/Urea or oxidation catalysts (DOC), which reduce particulate emissions from diesel engines. The end products are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O), both of which are colorless, non-flammable, odorless and non-toxic.
Highly toxic substances such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) or even nitrogen oxides (NOX) have been effectively reduced since the 1980s thanks to catalytic converter technology, and fuels have been freed from lead and sulfur. In addition, increasingly better particulate filters in direct-injection engines ensure less soot and particulate matter in urban areas, and even the nitrogen oxide emissions of diesel engines, which are stronger in principle, have been reduced by over 90 percent through SCR and NOX storage catalytic converters, which reduce them chemically to nitrogen and water, for example by adding ammonia from a urea solution (AdBlue).
What are the challenges in exhaust gas cleaning?
One of the biggest challenges is the high temperatures of the exhaust gases, which can impair the efficiency of the exhaust gas aftertreatment system and damage surrounding components, so proper temperature management is crucial. In addition, the exhaust aftertreatment system must be designed to be robust and durable enough to function optimally and operate reliably even under extreme conditions and load conditions of the engine or plant.
There are also a variety of national and international regulations and standards that govern exhaust aftertreatment. The best known and most widely used regulation is the Euro emissions standard from the European Union, which regulates the emission of vehicle pollutants. The Euro 6d standard has been in place since 2021 and is set to be replaced by the Euro 7 standard in 2025. Euro standards are renewed every couple of years to keep up with the latest technological developments. There are also specific regulations for certain industries, such as aviation or shipping, which vary from country to country.
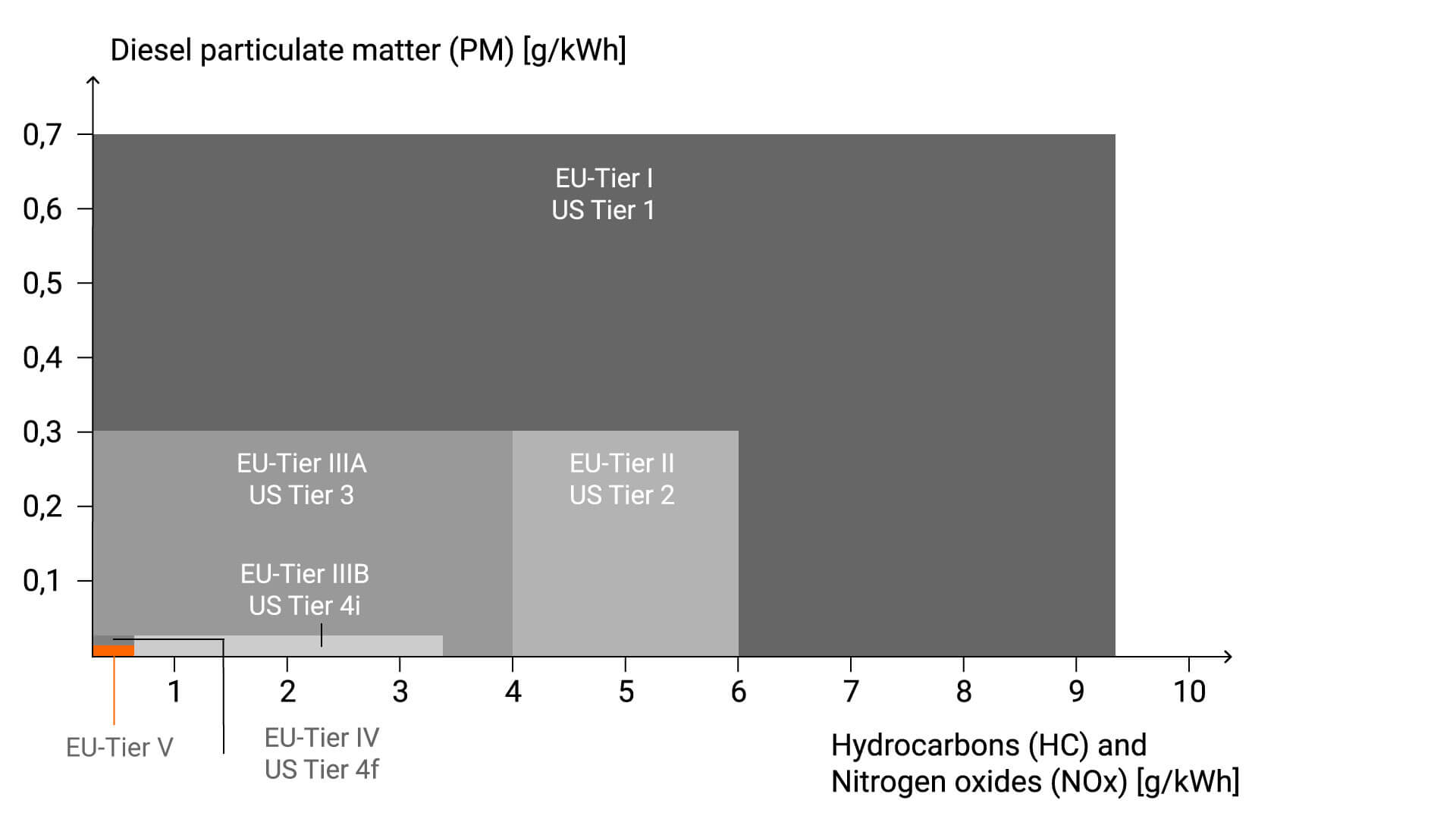
Source: Exhaust Gas Legislation Diesel and Gas Engines, VDMA, 2017
How can a high-temperature insulation improve exhaust gas aftertreatment?
The exhaust tract requires high temperatures to ensure smooth operation. To achieve this, exhaust pipes must be insulated to suit the specific application. A high-temperature insulation can help improve exhaust gas aftertreatment by reducing heat losses and making the exhaust gas temperature more controllable, increasing the efficiency of exhaust gas purification, and extending the service life of components.
Maintaining optimal exhaust gas temperatures optimizes the heating behavior of exhaust aftertreatment systems (light off), reduces temperature fluctuations in the system during changing operating conditions, and thus increases the efficiency of the exhaust system. It also protects surrounding components from high temperatures and provides correspondingly effective fire protection and contact protection.
tmax insulation solutions ensure that optimum temperatures prevail at all points in the exhaust tract, thus contributing to compliance with strict exhaust gas standards and improved exhaust gas values.
- Reduction of heat losses
- Optimal temperature management
- Increased efficiency and performance of exhaust aftertreatment systems
- Improved exhaust gas values
Where are insulations for exhaust gas aftertreatment used?
High-temperature insulations are used in a wide range of applications in exhaust gas aftertreatment. In the automotive industry, high-temperature insulations are used to protect the catalytic converter and diesel particulate filter from excessive temperatures, and in power generation, high-temperature insulations are used to protect the exhaust components of power plants.
Thermal insulations from tmax maintain the necessary process heat in place in the system – turbocharger, manifold, exhaust pipes, DPF, SCR, etc. – and thus make a decisive contribution to more efficient exhaust gas aftertreatment.
A wide product range of different insulation and insulating materials makes it possible to solve any challenge in the high-temperature range.
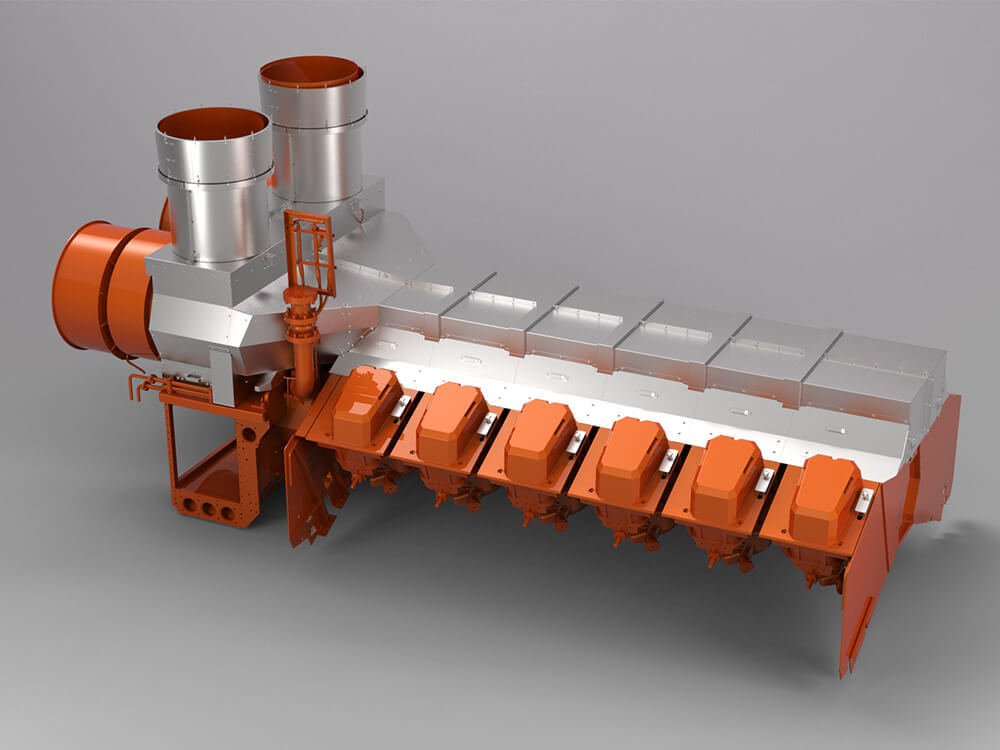 |
 |
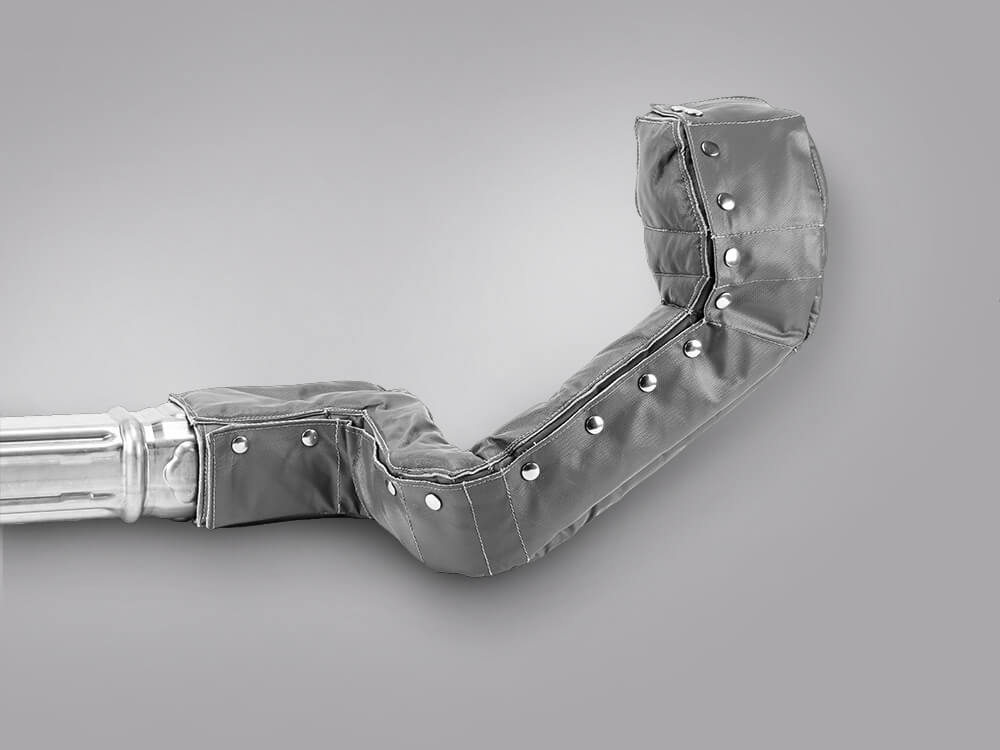 |
| Metal exhaust pipe insulation from tmax | Foil exhaust pipe insulation from tmax | Textile exhaust pipe insulation from tmax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
High-temperature insulation can help make exhaust gas aftertreatment more effective, reliable and cost-efficient. It can also help reduce maintenance and replacement costs by extending the service life of exhaust gas purification components and increasing plant uptime.
With tmax high-temperature insulation, optimum temperatures prevail at all points in the exhaust tract – in short, maximum efficient exhaust gas aftertreatment.
- Reduction of heat losses
- Optimum temperature management
- Increased efficiency and performance of exhaust gas aftertreatment
- Improved exhaust gas values
Categories
Temperatures under control.
Discover the world of insulation and how tmax, as a market leader, will also solve your requirements.

